Distribution
on Math
1. continuous probability Distribution
probability distribution that has a cumulative distribution function that is continuous
- normal distribution(= Gaussian normal distribution)
- standard normal distribution
when ${\displaystyle \mu =0}$ and ${\displaystyle \sigma =1}$

- central limit Theorem
when independent random variables are added, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed
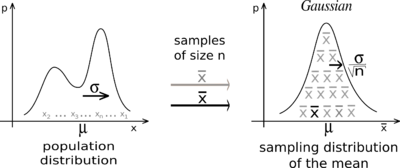
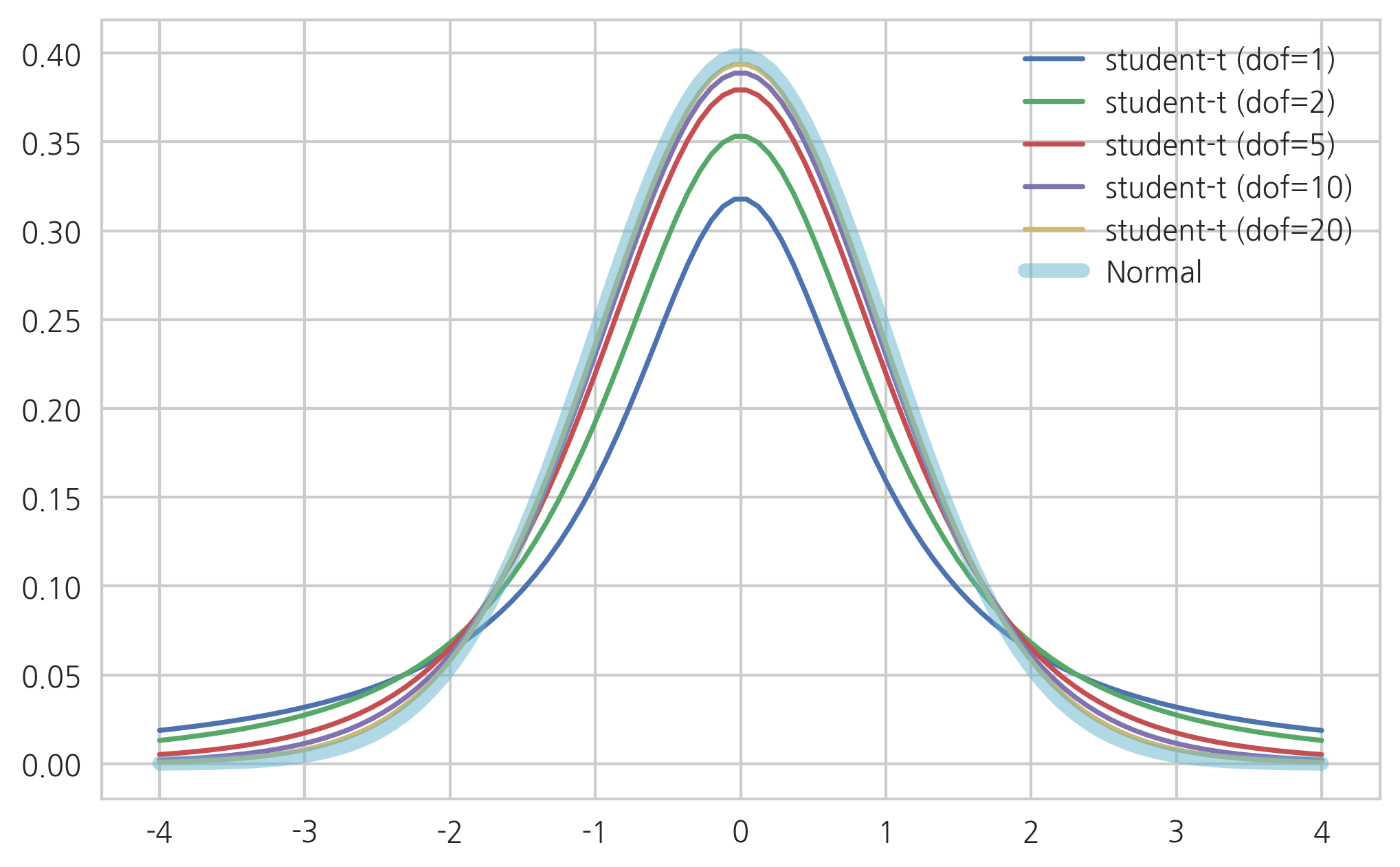
- Student t distribution
any member of a family of continuous probability distributions that arises when estimating the mean of a normally distributed population in situations where the sample size is small and population standard deviation is unknown
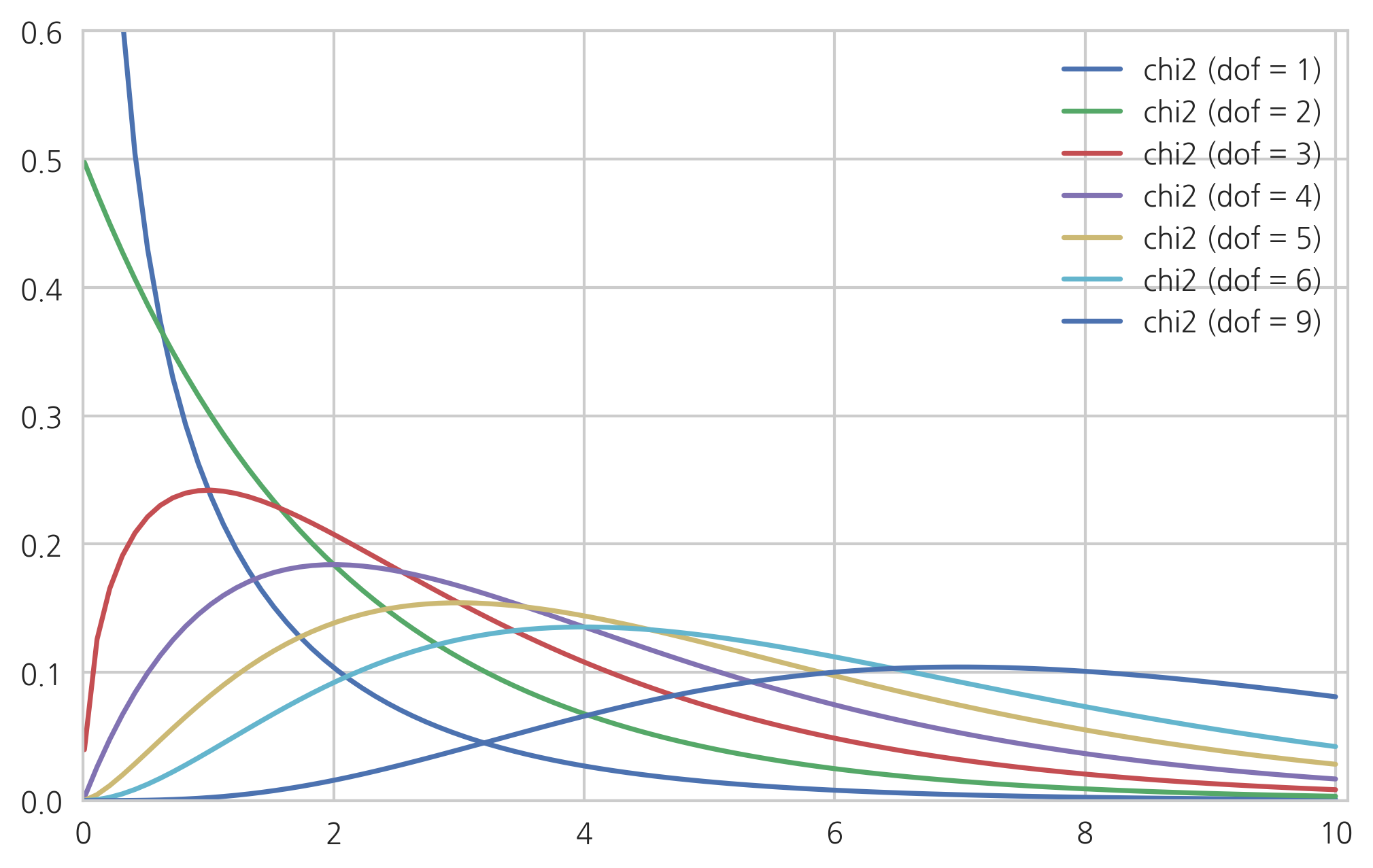
- chi-squared distribution
the distribution of a sum of the squares of k independent standard normal random variables
- F-distribution
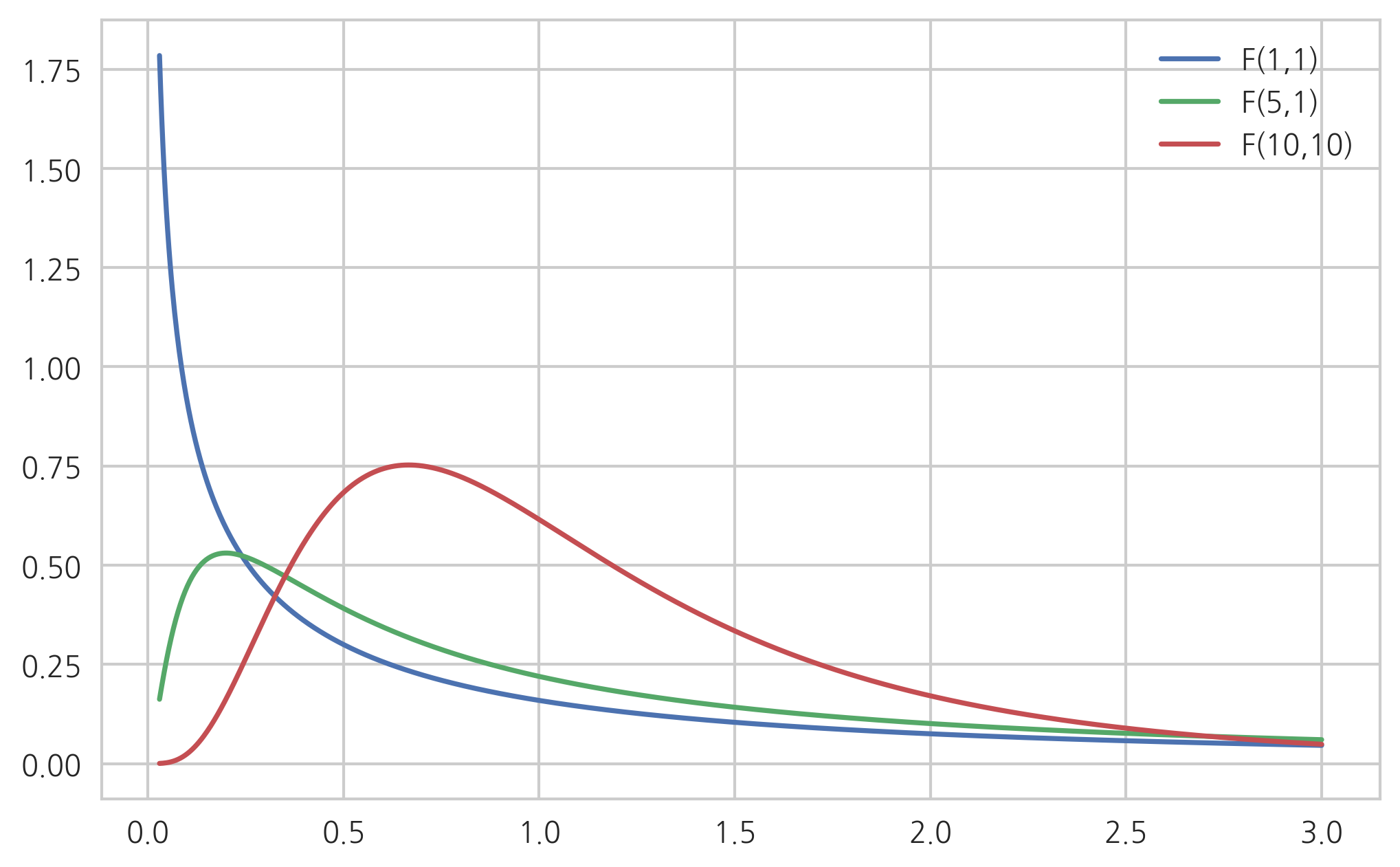
2. Discrete probability Distribution
probability distribution characterized by a probability mass function
- Bernoulli Distribution
- Binomial Distribution
- Categorical distribution
- Multinomial distribution
3. Bayesian Estimator
an estimator or decision rule that minimizes the posterior expected value of a loss function
- Beta distribution
- Dirichlet distribution
- Gamma distribution
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_distribution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_limit_theorem
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student%27s_t-distribution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chi-squared_distribution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/F-distribution