Bayesian Theorem
on Math
1. state of theorem
- prior probability
the initial degree of belief in A
- likelihood probability
- poterior probability
the probability for A after taking into account B for and against A
2. conditaional probability
conditional probability, the likelihood of event A occurring given that B is true
conditional probability, the likelihood of event B occurring given that A is true
marginal probability
- memorable form
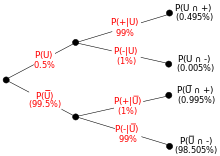
3. drug test example
Suppose that a test for using a particular drug is 99% sensitive and 99% specific. That is, the test will produce 99% true positive results for drug users and 99% true negative results for non-drug users. Suppose that 0.5% of people are users of the drug. What is the probability that a randomly selected individual with a positive test is a drug user?
Reference